Quick Start User Guide
Overview
Slurm is an open source,
fault-tolerant, and highly scalable cluster management and job scheduling system
for large and small Linux clusters.
Slurmは、大小のLinuxクラスター向けのオープンソースでフォールトトレラントで拡張性の高いクラスター管理およびジョブスケジューリングシステムです。
Slurm requires no kernel modifications for
its operation and is relatively self-contained.
Slurmは、その操作にカーネルの変更を必要とせず、比較的自己完結型です。
As a cluster workload manager,
Slurm has three key functions.
クラスターワークロードマネージャーとして、Slurmには3つの主要な機能があります。
First, it allocates exclusive and/or non-exclusive
access to resources (compute nodes) to users for some duration of time so they
can perform work.
まず、リソース(計算ノード)への排他的および/または非排他的アクセスを一定期間ユーザーに割り当てて、ユーザーが作業を実行できるようにします。
Second, it provides a framework for starting, executing, and
monitoring work (normally a parallel job) on the set of allocated nodes.
次に、割り当てられたノードのセットで作業(通常は並列ジョブ)を開始、実行、および監視するためのフレームワークを提供します。
Finally,
it arbitrates contention for resources by managing a queue of pending work.
最後に、保留中の作業のキューを管理することにより、リソースの競合を調停します。
Architecture
As depicted in Figure 1, Slurm consists of a slurmd daemon running on
each compute node and a central slurmctld daemon running on a management node
(with optional fail-over twin).
図1に示すように、Slurmは、各計算ノードで実行されるslurmdデーモンと、管理ノードで実行される中央のslurmctldデーモン(オプションのフェイルオーバーツインを使用)で構成されます。
The slurmd daemons provide fault-tolerant hierarchical communications.
slurmdデーモンは、フォールトトレラントな階層通信を提供します。
The user commands include: sacct, salloc, sattach,
sbatch, sbcast, scancel, scontrol,
sinfo, sprio, squeue, srun,
sshare, sstat, strigger and sview.
ユーザーコマンドには、sacct、salloc、sattach、sbatch、sbcast、scancel、scontrol、sinfo、sprio、squeue、srun、sshare、sstat、strigger、sviewが含まれます。
All of the commands can run anywhere in the cluster.
すべてのコマンドは、クラスター内のどこでも実行できます。
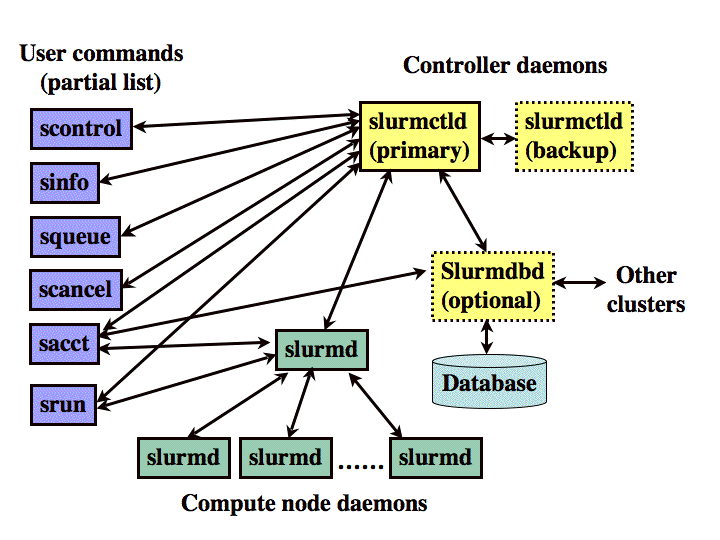 Figure 1. Slurm components
Figure 1. Slurm components
The entities managed by these Slurm daemons, shown in Figure 2, include
nodes, the compute resource in Slurm,
partitions, which group nodes into logical (possibly overlapping) sets,
jobs, or allocations of resources assigned to a user for
a specified amount of time, and
job steps, which are sets of (possibly parallel) tasks within a job.
図2に示すように、これらのSlurmデーモンによって管理されるエンティティには、ノード、Slurmの計算リソース、ノードを論理(重複している可能性がある)セットにグループ化するパーティション、ジョブ、または指定された量のユーザーに割り当てられたリソースの割り当てが含まれます。時間、およびジョブステップ。これらは、ジョブ内の(場合によっては並列の)タスクのセットです。
The partitions can be considered job queues, each of which has an assortment of
constraints such as job size limit, job time limit, users permitted to use it, etc.
パーティションはジョブキューと見なすことができ、各パーティションには、ジョブサイズの制限、ジョブの時間制限、使用を許可されているユーザーなど、さまざまな制約があります。
Priority-ordered jobs are allocated nodes within a partition until the resources
(nodes, processors, memory, etc.) within that partition are exhausted.
優先順位の高いジョブには、パーティション内のリソース(ノード、プロセッサ、メモリなど)が使い果たされるまで、パーティション内のノードが割り当てられます。
Once
a job is assigned a set of nodes, the user is able to initiate parallel work in
the form of job steps in any configuration within the allocation.
ジョブにノードのセットが割り当てられると、ユーザーは、割り当て内の任意の構成でジョブステップの形式で並列作業を開始できます。
For instance,
a single job step may be started that utilizes all nodes allocated to the job,
or several job steps may independently use a portion of the allocation.
たとえば、ジョブに割り当てられたすべてのノードを利用する単一のジョブステップを開始したり、複数のジョブステップが割り当ての一部を個別に使用したりできます。
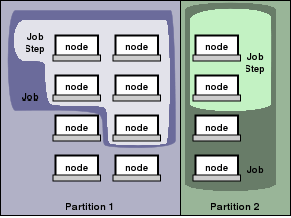 Figure 2. Slurm entities
Figure 2. Slurm entities
Commands
Man pages exist for all Slurm daemons, commands, and API functions.
すべてのSlurmデーモン、コマンド、およびAPI関数のマニュアルページが存在します。
The command
option --help also provides a brief summary of
options.
コマンドオプション--helpは、オプションの簡単な要約も提供します。
Note that the command options are all case sensitive.
コマンドオプションではすべて大文字と小文字が区別されることに注意してください。
sacct is used to report job or job
step accounting information about active or completed jobs.
sacctは、アクティブまたは完了したジョブに関するジョブまたはジョブステップのアカウンティング情報を報告するために使用されます。
salloc is used to allocate resources
for a job in real time.
sallocは、ジョブにリソースをリアルタイムで割り当てるために使用されます。
Typically this is used to allocate resources and spawn a shell.
通常、これはリソースを割り当ててシェルを生成するために使用されます。
The shell is then used to execute srun commands to launch parallel tasks.
次に、シェルを使用してsrunコマンドを実行し、並列タスクを起動します。
sattach is used to attach standard
input, output, and error plus signal capabilities to a currently running
job or job step.
sattachは、現在実行中のジョブまたはジョブステップに、標準の入力、出力、およびエラーと信号の機能をアタッチするために使用されます。
One can attach to and detach from jobs multiple times.
ジョブに何度もアタッチしたり、ジョブからデタッチしたりできます。
sbatch is used to submit a job script
for later execution.
sbatchは、後で実行するためにジョブスクリプトを送信するために使用されます。
The script will typically contain one or more srun commands
to launch parallel tasks.
スクリプトには通常、並列タスクを起動するための1つ以上のsrunコマンドが含まれます。
sbcast is used to transfer a file
from local disk to local disk on the nodes allocated to a job.
sbcastは、ジョブに割り当てられたノード上のローカルディスクからローカルディスクにファイルを転送するために使用されます。
This can be
used to effectively use diskless compute nodes or provide improved performance
relative to a shared file system.
これを使用して、ディスクレス計算ノードを効果的に使用したり、共有ファイルシステムに比べてパフォーマンスを向上させたりできます。
scancel is used to cancel a pending
or running job or job step.
scancelは、保留中または実行中のジョブまたはジョブステップをキャンセルするために使用されます。
It can also be used to send an arbitrary signal to
all processes associated with a running job or job step.
また、実行中のジョブまたはジョブステップに関連付けられているすべてのプロセスに任意のシグナルを送信するために使用することもできます。
scontrol is the administrative tool
used to view and/or modify Slurm state.
scontrolは、Slurmの状態を表示および/または変更するために使用される管理ツールです。
Note that many scontrol
commands can only be executed as user root.
多くのscontrolコマンドは、ユーザーrootとしてのみ実行できることに注意してください。
sinfo reports the state of partitions
and nodes managed by Slurm.
sinfoは、Slurmによって管理されているパーティションとノードの状態を報告します。
It has a wide variety of filtering, sorting, and formatting
options.
さまざまなフィルタリング、並べ替え、およびフォーマットのオプションがあります。
sprio is used to display a detailed
view of the components affecting a job's priority.
sprioは、ジョブの優先度に影響を与えるコンポーネントの詳細ビューを表示するために使用されます。
squeue reports the state of jobs or
job steps.
squeueは、ジョブまたはジョブステップの状態を報告します。
It has a wide variety of filtering, sorting, and formatting options.
さまざまなフィルタリング、並べ替え、およびフォーマットのオプションがあります。
By default, it reports the running jobs in priority order and then the pending
jobs in priority order.
デフォルトでは、実行中のジョブを優先順位で報告し、次に保留中のジョブを優先順位で報告します。
srun is used to submit a job for
execution or initiate job steps in real time.
srunは、実行のためにジョブを送信したり、リアルタイムでジョブステップを開始したりするために使用されます。
srun
has a wide variety of options to specify resource requirements, including: minimum
and maximum node count, processor count, specific nodes to use or not use, and
specific node characteristics (so much memory, disk space, certain required
features, etc.).
srunには、リソース要件を指定するためのさまざまなオプションがあります。これには、最小および最大ノード数、プロセッサ数、使用するまたは使用しない特定のノード、特定のノード特性(メモリ、ディスクスペース、特定の必要な機能など)が含まれます。 。
A job can contain multiple job steps executing sequentially or in parallel on
independent or shared resources within the job's node allocation.
ジョブには、ジョブのノード割り当て内の独立したリソースまたは共有リソースで順次または並行して実行される複数のジョブステップを含めることができます。
sshare displays detailed information
about fairshare usage on the cluster.
sshareは、クラスターでのフェアシェアの使用に関する詳細情報を表示します。
Note that this is only viable when using
the priority/multifactor plugin.
これは、priority / multifactorプラグインを使用する場合にのみ実行可能であることに注意してください。
sstat is used to get information
about the resources utilized by a running job or job step.
sstatは、実行中のジョブまたはジョブステップで使用されているリソースに関する情報を取得するために使用されます。
strigger is used to set, get or
view event triggers.
striggerは、イベントトリガーを設定、取得、または表示するために使用されます。
Event triggers include things such as nodes going down
or jobs approaching their time limit.
イベントトリガーには、ノードがダウンしたり、ジョブが制限時間に近づいたりすることが含まれます。
sview is a graphical user interface to
get and update state information for jobs, partitions, and nodes managed by Slurm.
sviewは、Slurmによって管理されるジョブ、パーティション、およびノードの状態情報を取得および更新するためのグラフィカルユーザーインターフェイスです。
Examples
First we determine what partitions exist on the system, what nodes
they include, and general system state.
まず、システムに存在するパーティション、それらに含まれるノード、および一般的なシステム状態を判別します。
This information is provided
by the sinfo command.
この情報は、sinfoコマンドによって提供されます。
In the example below we find there are two partitions: debug
and batch.
以下の例では、デバッグとバッチの2つのパーティションがあることがわかります。
The * following the name debug indicates this is the
default partition for submitted jobs.
名前debugに続く*は、これが送信されたジョブのデフォルトのパーティションであることを示します。
We see that both partitions are in an UP state.
両方のパーティションがUP状態になっていることがわかります。
Some configurations may include partitions for larger jobs
that are DOWN except on weekends or at night.
一部の構成には、週末または夜間を除いてダウンしている大規模なジョブ用のパーティションが含まれる場合があります。
The information
about each partition may be split over more than one line so that
nodes in different states can be identified.
各パーティションに関する情報は、異なる状態のノードを識別できるように、複数の行に分割される場合があります。
In this case, the two nodes adev[1-2] are down.
この場合、2つのノードadev [1-2]がダウンしています。
The * following the state down indicate the nodes are
not responding.
状態が下がった後の*は、ノードが応答していないことを示します。
Note the use of a concise expression for node
name specification with a common prefix adev and numeric
ranges or specific numbers identified.
共通の接頭辞adevと数値範囲または特定の数値が識別された、ノード名の指定に簡潔な式を使用していることに注意してください。
This format allows for
very large clusters to be easily managed.
この形式では、非常に大きなクラスターを簡単に管理できます。
The sinfo command
has many options to easily let you view the information of interest
to you in whatever format you prefer.
sinfoコマンドには、関心のある情報を好きな形式で簡単に表示できるようにするための多くのオプションがあります。
See the man page for more information.
詳細については、manページを参照してください。
adev0: sinfo PARTITION AVAIL TIMELIMIT NODES STATE NODELIST debug* up 30:00 2 down* adev[1-2] debug* up 30:00 3 idle adev[3-5] batch up 30:00 3 down* adev[6,13,15] batch up 30:00 3 alloc adev[7-8,14] batch up 30:00 4 idle adev[9-12]
Next we determine what jobs exist on the system using the
squeue command.
次に、squeueコマンドを使用して、システムに存在するジョブを判別します。
The
ST field is job state.
STフィールドはジョブの状態です。
Two jobs are in a running state (R is an abbreviation
for Running) while one job is in a pending state
(PD is an abbreviation for Pending).
2つのジョブが実行状態(RはRunningの略語)で、1つのジョブが保留状態(PDはPendingの略語)です。
The TIME field shows how long the jobs have run
for using the format days-hours:minutes:seconds.
TIMEフィールドは、days-hours:minutes:secondsの形式を使用してジョブが実行された時間を示します。
The NODELIST(REASON) field indicates where the
job is running or the reason it is still pending.
NODELIST(REASON)フィールドは、ジョブが実行されている場所、またはジョブがまだ保留中の理由を示します。
Typical
reasons for pending jobs are Resources (waiting
for resources to become available) and Priority
(queued behind a higher priority job).
保留中のジョブの一般的な理由は、リソース(リソースが使用可能になるのを待機している)と優先度(優先度の高いジョブの後ろにキューに入れられている)です。
The squeue command
has many options to easily let you view the information of interest
to you in whatever format you prefer.
squeueコマンドには多くのオプションがあり、関心のある情報を好きな形式で簡単に表示できます。
See the man page for more information.
詳細については、manページを参照してください。
adev0: squeue JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON) 65646 batch chem mike R 24:19 2 adev[7-8] 65647 batch bio joan R 0:09 1 adev14 65648 batch math phil PD 0:00 6 (Resources)
The scontrol command
can be used to report more detailed information about
nodes, partitions, jobs, job steps, and configuration.
scontrolコマンドを使用して、ノード、パーティション、ジョブ、ジョブステップ、および構成に関するより詳細な情報をレポートできます。
It can also be used by system administrators to make
configuration changes.
また、システム管理者が構成を変更するために使用することもできます。
A couple of examples are shown
below.
いくつかの例を以下に示します。
See the man page for more information.
詳細については、manページを参照してください。
adev0: scontrol show partition PartitionName=debug TotalNodes=5 TotalCPUs=40 RootOnly=NO Default=YES OverSubscribe=FORCE:4 PriorityTier=1 State=UP MaxTime=00:30:00 Hidden=NO MinNodes=1 MaxNodes=26 DisableRootJobs=NO AllowGroups=ALL Nodes=adev[1-5] NodeIndices=0-4 PartitionName=batch TotalNodes=10 TotalCPUs=80 RootOnly=NO Default=NO OverSubscribe=FORCE:4 PriorityTier=1 State=UP MaxTime=16:00:00 Hidden=NO MinNodes=1 MaxNodes=26 DisableRootJobs=NO AllowGroups=ALL Nodes=adev[6-15] NodeIndices=5-14 adev0: scontrol show node adev1 NodeName=adev1 State=DOWN* CPUs=8 AllocCPUs=0 RealMemory=4000 TmpDisk=0 Sockets=2 Cores=4 Threads=1 Weight=1 Features=intel Reason=Not responding [slurm@06/02-14:01:24] 65648 batch math phil PD 0:00 6 (Resources) adev0: scontrol show job JobId=65672 UserId=phil(5136) GroupId=phil(5136) Name=math Priority=4294901603 Partition=batch BatchFlag=1 AllocNode:Sid=adev0:16726 TimeLimit=00:10:00 ExitCode=0:0 StartTime=06/02-15:27:11 EndTime=06/02-15:37:11 JobState=PENDING NodeList=(null) NodeListIndices= NumCPUs=24 ReqNodes=1 ReqS:C:T=1-65535:1-65535:1-65535 OverSubscribe=1 Contiguous=0 CPUs/task=0 Licenses=(null) MinCPUs=1 MinSockets=1 MinCores=1 MinThreads=1 MinMemory=0 MinTmpDisk=0 Features=(null) Dependency=(null) Account=(null) Requeue=1 Reason=None Network=(null) ReqNodeList=(null) ReqNodeListIndices= ExcNodeList=(null) ExcNodeListIndices= SubmitTime=06/02-15:27:11 SuspendTime=None PreSusTime=0 Command=/home/phil/math WorkDir=/home/phil
It is possible to create a resource allocation and launch
the tasks for a job step in a single command line using the
srun command.
srunコマンドを使用して、単一のコマンドラインでリソース割り当てを作成し、ジョブステップのタスクを起動することができます。
Depending
upon the MPI implementation used, MPI jobs may also be
launched in this manner.
使用するMPI実装によっては、MPIジョブもこの方法で起動される場合があります。
See the MPI section for more MPI-specific information.
MPI固有の詳細については、MPIセクションを参照してください。
In this example we execute /bin/hostname
on three nodes (-N3) and include task numbers on the output (-l).
この例では、3つのノード(-N3)で/ bin / hostnameを実行し、出力(-l)にタスク番号を含めます。
The default partition will be used.
デフォルトのパーティションが使用されます。
One task per node will be used by default.
デフォルトでは、ノードごとに1つのタスクが使用されます。
Note that the srun command has
many options available to control what resource are allocated
and how tasks are distributed across those resources.
srunコマンドには、割り当てられるリソースと、それらのリソース間でタスクを分散する方法を制御するために使用できる多くのオプションがあることに注意してください。
adev0: srun -N3 -l /bin/hostname 0: adev3 1: adev4 2: adev5
This variation on the previous example executes
/bin/hostname in four tasks (-n4).
前の例のこのバリエーションは、4つのタスク(-n4)で/ bin / hostnameを実行します。
One processor per task will be used by default (note that we don't specify
a node count).
デフォルトでは、タスクごとに1つのプロセッサが使用されます(ノード数は指定しないことに注意してください)。
adev0: srun -n4 -l /bin/hostname 0: adev3 1: adev3 2: adev3 3: adev3
One common mode of operation is to submit a script for later execution.
一般的な操作モードの1つは、後で実行するためにスクリプトを送信することです。
In this example the script name is my.script and we explicitly use
the nodes adev9 and adev10 (-w "adev[9-10]", note the use of a
node range expression).
この例では、スクリプト名はmy.scriptであり、ノードadev9とadev10を明示的に使用します(-w "adev [9-10]"、ノード範囲式の使用に注意してください)。
We also explicitly state that the subsequent job steps will spawn four tasks
each, which will ensure that our allocation contains at least four processors
(one processor per task to be launched).
また、後続のジョブステップでそれぞれ4つのタスクが生成されることを明示的に示します。これにより、割り当てに少なくとも4つのプロセッサが含まれるようになります(起動するタスクごとに1つのプロセッサ)。
The output will appear in the file my.stdout ("-o my.stdout").
出力はファイルmy.stdout( "-o my.stdout")に表示されます。
This script contains a timelimit for the job embedded within itself.
このスクリプトには、それ自体に埋め込まれたジョブの時間制限が含まれています。
Other options can be supplied as desired by using a prefix of "#SBATCH" followed
by the option at the beginning of the script (before any commands to be executed
in the script).
スクリプトの先頭(スクリプトで実行されるコマンドの前)にオプションを続けて「#SBATCH」のプレフィックスを使用することにより、必要に応じて他のオプションを指定できます。
Options supplied on the command line would override any options specified within
the script.
コマンドラインで指定されたオプションは、スクリプト内で指定されたオプションを上書きします。
Note that my.script contains the command /bin/hostname
that executed on the first node in the allocation (where the script runs) plus
two job steps initiated using the srun command
and executed sequentially.
my.scriptには、割り当ての最初のノード(スクリプトが実行される場所)で実行されたコマンド/ bin / hostnameと、srunコマンドを使用して開始されて順次実行される2つのジョブステップが含まれていることに注意してください。
adev0: cat my.script #!/bin/sh #SBATCH --time=1 /bin/hostname srun -l /bin/hostname srun -l /bin/pwd adev0: sbatch -n4 -w "adev[9-10]" -o my.stdout my.script sbatch: Submitted batch job 469 adev0: cat my.stdout adev9 0: adev9 1: adev9 2: adev10 3: adev10 0: /home/jette 1: /home/jette 2: /home/jette 3: /home/jette
The final mode of operation is to create a resource allocation
and spawn job steps within that allocation.
最後の操作モードは、リソース割り当てを作成し、その割り当て内にジョブステップを生成することです。
The salloc command is used
to create a resource allocation and typically start a shell within
that allocation.
sallocコマンドは、リソース割り当てを作成し、通常、その割り当て内でシェルを開始するために使用されます。
One or more job steps would typically be executed within that allocation
using the srun command to launch the tasks
(depending upon the type of MPI being used, the launch mechanism may
differ, see MPI details below).
通常、1つ以上のジョブステップがsrunコマンドを使用してその割り当て内で実行され、タスクが起動されます(使用されているMPIのタイプによって、起動メカニズムが異なる場合があります。以下のMPIの詳細を参照してください)。
Finally the shell created by salloc would
be terminated using the exit command.
最後に、sallocによって作成されたシェルは、exitコマンドを使用して終了します。
Slurm does not automatically migrate executable or data files
to the nodes allocated to a job.
Slurmは、実行可能ファイルまたはデータファイルをジョブに割り当てられたノードに自動的に移行しません。
Either the files must exists on local disk or in some global file system
(e.g. NFS or Lustre).
ファイルは、ローカルディスクまたはグローバルファイルシステム(NFSやLustreなど)に存在する必要があります。
We provide the tool sbcast to transfer
files to local storage on allocated nodes using Slurm's hierarchical
communications.
Slurmの階層通信を使用して、割り当てられたノード上のローカルストレージにファイルを転送するためのツールsbcastを提供します。
In this example we use sbcast to transfer
the executable program a.out to /tmp/joe.a.out on local storage
of the allocated nodes.
この例では、sbcastを使用して、割り当てられたノードのローカルストレージ上の実行可能プログラムa.outを/tmp/joe.a.outに転送します。
After executing the program, we delete it from local storage
プログラムを実行した後、ローカルストレージから削除します
tux0: salloc -N1024 bash $ sbcast a.out /tmp/joe.a.out Granted job allocation 471 $ srun /tmp/joe.a.out Result is 3.14159 $ srun rm /tmp/joe.a.out $ exit salloc: Relinquishing job allocation 471
In this example, we submit a batch job, get its status, and cancel it.
この例では、バッチジョブを送信し、そのステータスを取得して、キャンセルします。
adev0: sbatch test srun: jobid 473 submitted adev0: squeue JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON) 473 batch test jill R 00:00 1 adev9 adev0: scancel 473 adev0: squeue JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
Best Practices, Large Job Counts
Consider putting related work into a single Slurm job with multiple job
steps both for performance reasons and ease of management.
パフォーマンス上の理由と管理のしやすさの両方の理由から、関連する作業を複数のジョブステップを持つ単一のSlurmジョブに入れることを検討してください。
Each Slurm job can contain a multitude of job steps and the overhead in
Slurm for managing job steps is much lower than that of individual jobs.
各Slurmジョブには多数のジョブステップを含めることができ、ジョブステップを管理するためのSlurmのオーバーヘッドは個々のジョブのオーバーヘッドよりもはるかに低くなります。
Job arrays are an efficient mechanism of
managing a collection of batch jobs with identical resource requirements.
ジョブ配列は、同じリソース要件を持つバッチジョブのコレクションを管理する効率的なメカニズムです。
Most Slurm commands can manage job arrays either as individual elements (tasks)
or as a single entity (e.g. delete an entire job array in a single command).
ほとんどのSlurmコマンドは、ジョブ配列を個々の要素(タスク)または単一のエンティティとして管理できます(たとえば、単一のコマンドでジョブ配列全体を削除します)。
MPI
MPI use depends upon the type of MPI being used.
MPIの使用は、使用されているMPIのタイプによって異なります。
There are three fundamentally different modes of operation used
by these various MPI implementation.
これらのさまざまなMPI実装で使用される3つの根本的に異なる動作モードがあります。
- Slurm directly launches the tasks and performs initialization of
communications through the PMI2 or PMIx APIs.
Slurmはタスクを直接起動し、PMI2またはPMIxAPIを介して通信の初期化を実行します。
(Supported by most modern MPI implementations.)
(最新のMPI実装でサポートされています。) - Slurm creates a resource allocation for the job and then
mpirun launches tasks using Slurm's infrastructure (older versions of
OpenMPI).
Slurmはジョブのリソース割り当てを作成し、mpirunはSlurmのインフラストラクチャ(古いバージョンのOpenMPI)を使用してタスクを起動します。 - Slurm creates a resource allocation for the job and then
mpirun launches tasks using some mechanism other than Slurm,
such as SSH or RSH.
Slurmはジョブのリソース割り当てを作成し、mpirunはSSHやRSHなどのSlurm以外のメカニズムを使用してタスクを起動します。
These tasks initiated outside of Slurm's monitoring or control.
これらのタスクは、Slurmの監視または制御の外部で開始されました。
Slurm's epilog should be configured to purge these tasks when the job's allocation is relinquished.
Slurmのエピローグは、ジョブの割り当てが放棄されたときにこれらのタスクをパージするように構成する必要があります。
The use of pam_slurm_adopt is also strongly recommended.
pam_slurm_adoptの使用も強くお勧めします。
Links to instructions for using several varieties of MPI
with Slurm are provided below.
Slurmでいくつかの種類のMPIを使用するための手順へのリンクを以下に示します。
Last modified 19 November 2019